GZDW-1 Dual Backup Energy saving Parallel DC Power Supply System
The GZDW-1 dual backup energy-saving parallel DC power supply system produced by our company is suitable for substations, power plants, various power engineering projects, and places that require different voltage levels of backup power. It serves as a power source for and controls high-voltage switches, relay protection, and automation devices, and can easily achieve four major functions: telemetry, remote control, remote signaling, and remote adjustment.
Product Features
Adopting parallel current sharing technology, with strong applicability, the number of batteries can be selected according to the load situation. The unique battery monitoring module can automatically activate units with batteries or a set of dual batteries, fully activating the battery’s activity and increasing its lifespan by 3-5 times.
DC systems with 100AH and below can be arranged in one cabinet without the need for a separate battery cabinet.
The charging module can automatically activate, monitor, and alarm a single battery or a group of dual batteries. It can sample and analyze the usage and parameters of the batteries to accurately diagnose faults and facilitate maintenance.
The product adopts multiple transmission methods to connect with the backend, and monitors the module and battery status in real-time.
In addition to the dual circuit incoming line system, the charging modules of the parallel DC system can also be mutually backup, thereby solving the problem of system failure caused by single module or single battery damage and improving the reliability of power consumption.
The voltage levels of the control bus and the combination bus are the same to avoid component explosion caused by incorrect wiring of the control bus and the combination bus.


Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
We are professional EV charger manufacturer.
This depends on the EV battery size, remaining battery capacity, and the type of EV charger used as well as environmental conditions such as temperature.Typically, an AC charger with an output power of 7–22 kW can fully charge an EV in between 3 and 6 hours.With a 50–200-kW DC fast charger, the charge time can be reduced to 10–60 minutes.
An AC charger provides AC power, which is then converted to DC power by an onboard charger inside the EV (before it reaches the battery). AC chargers are normally used in slow-charging applications such as home charging. A DC charger converts AC power from the grid into DC power, which is more efficient and supplies the batteries directly. Thus, the charging time is markedly shorter. DC chargers have higher power requirements and therefore a higher installation complexity. As such, the installation cost can be higher than that for an AC charger. DC systems are generally used in commercial/public charging applications where shorter dwell tines are needed
This depends on your situation. Fast DC chargers are ideal for cases where you need to recharge your EV quickly, such as at an intercity highway charging station or rest stop. An AC charger is suitable for places where you stay longer, such as workplace, shopping malls, cinema and at home.


























.png) PV-Storage-Charging
PV-Storage-Charging-1.png) High & Low Voltage Switchgear
High & Low Voltage Switchgear Company Profile
Company Profile News Information
News Information Service Support
Service Support Cloud Platform Customized Development
Cloud Platform Customized Development Leisheng Charging International Platform
Leisheng Charging International Platform Leisn Home Charging Platform
Leisn Home Charging Platform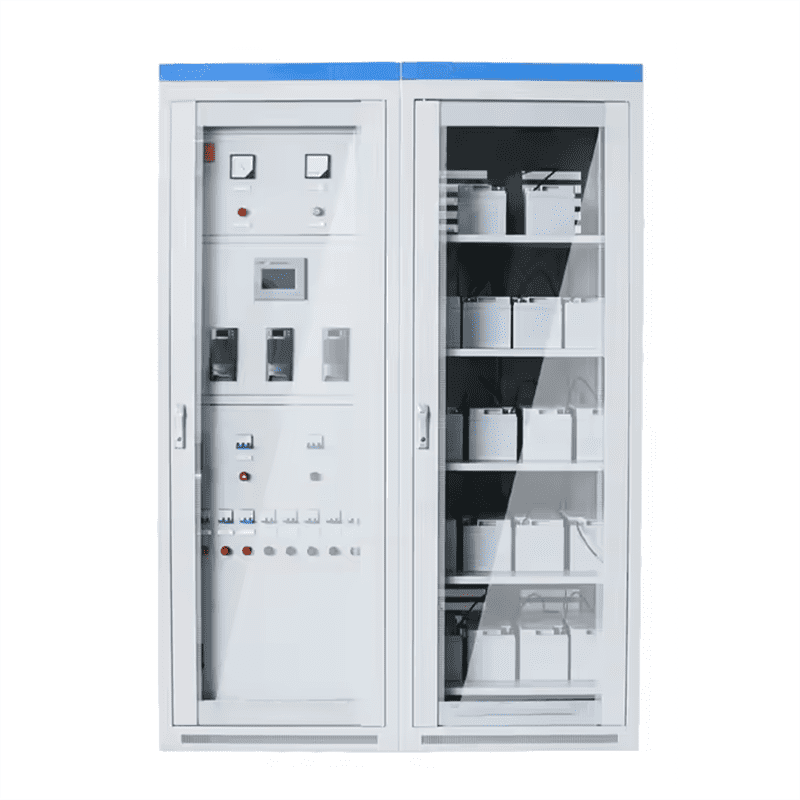













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.